Noncontrast head CT
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CB1087-Noncontrast head CT
 View Images
View Images
CB1087-Noncontrast head CT
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
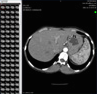
Extensive fracture of the left facial bones, left orbital apex/optic canal, left otomastoid, left greater & lesser sphenoid wings. There are inner bone table fractures of both frontal bones, both ethmoid bones and the roof of the left otomastoid bones.
Findings
Noncontrast head CT
There is a subdural hematoma with maximum width that outlines the left anterior temporal pole and then follows the low and mid convexity, lateral, temporal area. It produces only minimal mass effect with some compression of the temporal horn but no significant uncal herniation.
The subdural hematoma in the anterior temporal polar area overlies the left sphenoparietal sinus and there is a sphoid wing fracture in the same location. The subdural is very likely a venous diploic or venous sinus bleed.
There is a left basifrontal hemorrhage immediately above the left posterior ethmoid bridge fractures, which is likely related to a ethmoid spicules causing brain laceration.
Potentially, the left sphenoparietal sinus or the left superior sylvian vein are at risk for thrombosis from subdural, although that is more common from epidural hemorrhage associated with fracture of the greater sphenoid wing.
Impression
2. There are left intraorbital injuries with retroconal hemorrhages, probable Tenon's space hematoma, and ocular proptosis without obvious tenting.
3. There is a 4-5 mm subdural hematoma within the left anterior temporal fossa extending laterally along the basilar and low convexity of the temporal lobe. The does not produce uncal herniation.
Recommendations
No recommendation
