Acetabular fracture - CT (w/pelvic ring injury)
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CA0520-Acetabular fracture - CT (w/pelvic ring injury)
 View Images
View Images
CA0520-Acetabular fracture - CT (w/pelvic ring injury)
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
Findings
Findings
A pelvic binder is noted.
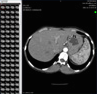
A pelvic ring injury is present. There is a coronally oriented fracture of the left posterior innominate bone. The posterior fragment maintains normal approximation to the sacrum. The anterior fragment is mildly externally rotated with associated widening of the anterior aspect of the left sacroiliac joint. Alignment of the right sacroiliac joint is within normal limits.
There is widening of the pubic symphysis measuring up to 2.1 cm. At the level of the pubic symphysis, the left hemipelvis is anterior in position with respect to the right, secondary to external rotation of the left hemipelvis as discussed above.
There is a transverse and posterior wall fracture of the right acetabulum. The transverse component extends through the weightbearing acetabular dome with displacement measuring at least 0.9 cm. The posterior wall component is comminuted. There is an isolated fragment containing posterior acetabular wall articular surface which is rotated 90 degrees and impacted. The articular surface contained by this fragment measures 2.0 x 1.4 cm. There is an additional nondisplaced posterior acetabular wall fracture component. There is an additional isolated fracture fragment involving the quadrilateral plate anteriorly.
Mild widening of the medial right hip joint space secondary to the presence of effusion/blood products. No mineralized intra-articular bodies noted within the right hip joint.
Blood products/edema within the superficial adipose layer along the right anterolateral pelvis extending into the right inguinal region. Blood products/edema along both pelvic sidewalls, left greater than right. No evidence for active contrast extravasation. Blood products about the bladder.
Bilateral L5 pars interarticularis defects are present. Minimal anterolisthesis of L5 on S1 and minimal retrolisthesis of L4 on L5.
Mild degenerative changes in the visualized lower lumbar spine, at both sacroiliac joints, and at the pubic symphysis. Well-corticated fragment in the left acetabular fossa, likely chronic given lack of adjacent intra-articular pathology at this site.
Impression
Transverse and posterior wall right acetabular fracture. Displaced fractures involve the weightbearing dome. The posterior wall component is comminuted. One of the isolated posterior wall fracture fragments is impacted and rotated.
Recommendations
CT cystogram.
