Generalized Probably Viral Sialadenitis, CT
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CA0371-Generalized Probably Viral Sialadenitis, CT
 View Images
View Images
CA0371-Generalized Probably Viral Sialadenitis, CT
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
Findings
Parotid Glands
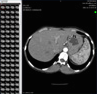
The right parotid gland is enlarged, with markedly abnormal enhancement. The left parotid gland is possibly abnormally swollen with borderline abnormal increased enhancement. There is extensive intraglandular parenchymal edema but no discrete fluid collections.
The parotid ducts and the intraglandular ducts are not dilated without evidence of intraductal stones other causes of obstruction.
There is extensive cellulitis within the fat surrounding the right parotid gland, extending to the adjacent masticator, parapharyngeal and submandibular spaces with thickening and infiltration of the SMAS.
Submandibular glands
The submandibular glands are also both enlarged and show abnormal enhancement. There is substantial parenchymal edema within both submandibular glands with no discrete fluid collections in the gland parenchyma. The submandibular ducts and the intraglandular ducts are not dilated and show no intraductal stones other causes of obstruction.
There is cellulitis within the submandibular space, more prominent on the right than left, extending into the neck and submental region. The overlying SMAS is thickened.
The lymph nodes in level 1A and 1B are reactive in nature.
Sublingual glands
The sublingual glands are not enlarged and do not show abnormal enhancement
Other findings
The lacrimal glands and both globes are normal.
Other significant abnormal findings are not present.
