Hemorrhage - Case 2 Head CT
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CB1681-Hemorrhage - Case 2 Head CT
 View Images
View Images
CB1681-Hemorrhage - Case 2 Head CT
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
Findings
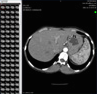
CT head noncontrast
There is a large (2 x 3 x 3cm) acute (CT hyper dense) hematoma in the right dorsal thalamus with perilesional edema. There is an additional 4 mm diameter acute parenchymal hematoma in the left posterior parietal lobe and a suspicious microhemorrhage in the left cerebellar dentate nucleus.
There is a small amount of intraventricular blood filling both occipital horns. There is no 4th ventricular or subarachnoid blood.
There is advanced, age-related cerebral atrophy and secondary (ex vacuo) ventriculomegaly. The right thalamic hematoma is not blocking the right lateral ventricle.
CT Head post contrast or CTA
The post contrast CT and CTA demonstrate no underlying causative event or tumoral lesion.
Impression
2. There is a small volume of blood in the occipital horns bilaterally.
3. There is prominent, age-related cortical atophic changes.
