AVM Case 4, MR
Claim CME CreditPOINT OF CARE INFORMATION
This CME activity consists of the student reviewing the video of the professor reviewing the case as well as the associated DICOM image set related to the case in question.
Learning Objectives
As a result of participation in this activity, participants should be able to:
- Provide improved patient care.
- Greater knowledge of the imaging characteristics of the patient's disease.
- Understand a better approach to interpretation of studies.
Faculty Disclosure
Mehmet Albayram, MD, Ivan Davis, MD, Mariam Hanna, MD, Anthony Mancuso, MD, Ronald Quisling, MD, Dhanashree Rajderkar, MD, Priya Sharma, MD, Roberta Slater, MD and Joann Stamm, MBA have disclosed that they have no relevant financial relationships. No one else is a position to control content have any financial relationship to disclose.
CME Advisory Committee Disclosure:
Conflict of interest information for the CME Advisory Committee members can be found on the following website: https://cme.ufl.edu/disclosure/.
Continuing Medical Education Credit
Accreditation: The University of Florida College of Medicine is accredited by the Accreditation Council for Continuing Medical Education (ACCME) to provide continuing medical education for physicians.
Credit: The University of Florida College of Medicine designates this enduring material for a maximum of 0.5 AMA PRA Category 1 Credits. Physicians should claim only the credit commensurate with the extent of their participation in the activity.
CB1660-AVM Case 4, MR
 View Images
View Images
CB1660-AVM Case 4, MR
Case ReportHistory
Exam
Prior Study
Findings
Findings:
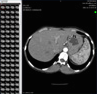
There is evidence of multicentric, angiomatous transformations (a variant of arteriovenous malformation) located in three separate areas. The largest area of involvement is in the right posterior frontal centrum semiovale. The other two are small lesions: one is along the posterior pulvinar and the other is in the left lateral basifrontal cortex. A distinct nidus is absent in each lesion. Rather the afferent feeding arteries appear dispersed between areas of brain parenchyma.
Evidence of the interpose brain parenchyma is most apparent on the T2-w sequence.
There is no evidence of recent nor prior hemorrhage.
Impression
Recommendations
No recommendation
